Project Title: INTERMETALLICS
Investigators: Leonid A. Bendersky and Shinji Mitao (guest scientist from NKK, Japan)
Technical Description:
In this research program we initiated the study of factors affecting stability of materials
having high density of interfaces. In particular, the study of initiation and development of
discontinuous coarsening (DC) in lamellar structures of the technologically important novel
TiAl-based alloys (gamma aluminides) was designed. Since the gamma aluminides are
designed for structural heat resistant applications (e.g., for aircraft engines), the structural
instability can be one of the factors that limits the application temperature. The research
program includes both an experimental (TEM, SEM, electron channeling) and theoretical
study.
Technical Objectives:
- Understanding the mechanisms of initiation of grain boundary instability in lamellar
grains.
- Understanding the mechanisms of growth of highly anisotropic lamellar structures.
- Understanding factors affecting DC, including (a) presence of grain boundary
allotriomorphs; (b) orientations of grain boundary with respect to the orientation of
lamellae; (c) effect of ternary alloying.
- Modification of Livingston-Cahn kinetic equations for the case of anisotropic lamellae.
Anticipated Outcome:
- Equations of DC growth for the anisotropic case of gamma aluminides.
- Ability to predict the beginning and extent of microstructural changes by DC.
- Optimization of microstructure for minimal DC, and, therefore, for higher application
temperatures.
- Fundamental understanding of migration of grain boundaries controlled by grain
boundary diffusion.
Accomplishments for FY 1995:
- Continuous and discontinuous coarsening of Ti3Al (
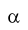 2)/TiAl (
2)/TiAl (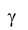 ) lamellae was studied
for binary Ti-Al alloys containing atomic fractions of Al at 40%, 44% and 47%, at
temperatures ranging from 900 oC to 1050 oC. Based on the experimental results, we
were able to identify different mechanisms of DC initiation. Kinetics of the
coarsening was analyzed using thermodynamic considerations of the chemical and
interfacial driving forces derived from non-equilibrium in primary lamellae formed by
Widmanstatten-type growth.
) lamellae was studied
for binary Ti-Al alloys containing atomic fractions of Al at 40%, 44% and 47%, at
temperatures ranging from 900 oC to 1050 oC. Based on the experimental results, we
were able to identify different mechanisms of DC initiation. Kinetics of the
coarsening was analyzed using thermodynamic considerations of the chemical and
interfacial driving forces derived from non-equilibrium in primary lamellae formed by
Widmanstatten-type growth.
- Equations of growth of the DC grains were obtained for the anisotropic case of
gamma aluminides by modifying Livingston and Cahn treatment.
- Three types of morphology in DC lamellar structure were identified and described.
Appearance of these morphologies was predicted by the developed modified equations.
 Back to Table of Contents
Back to Table of Contents
Last modified: Mon Jan 06 09:46:15 1997
Metallurgy Webmeister
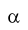 2)/TiAl (
2)/TiAl (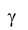 ) lamellae was studied
for binary Ti-Al alloys containing atomic fractions of Al at 40%, 44% and 47%, at
temperatures ranging from 900 oC to 1050 oC. Based on the experimental results, we
were able to identify different mechanisms of DC initiation. Kinetics of the
coarsening was analyzed using thermodynamic considerations of the chemical and
interfacial driving forces derived from non-equilibrium in primary lamellae formed by
Widmanstatten-type growth.
) lamellae was studied
for binary Ti-Al alloys containing atomic fractions of Al at 40%, 44% and 47%, at
temperatures ranging from 900 oC to 1050 oC. Based on the experimental results, we
were able to identify different mechanisms of DC initiation. Kinetics of the
coarsening was analyzed using thermodynamic considerations of the chemical and
interfacial driving forces derived from non-equilibrium in primary lamellae formed by
Widmanstatten-type growth.